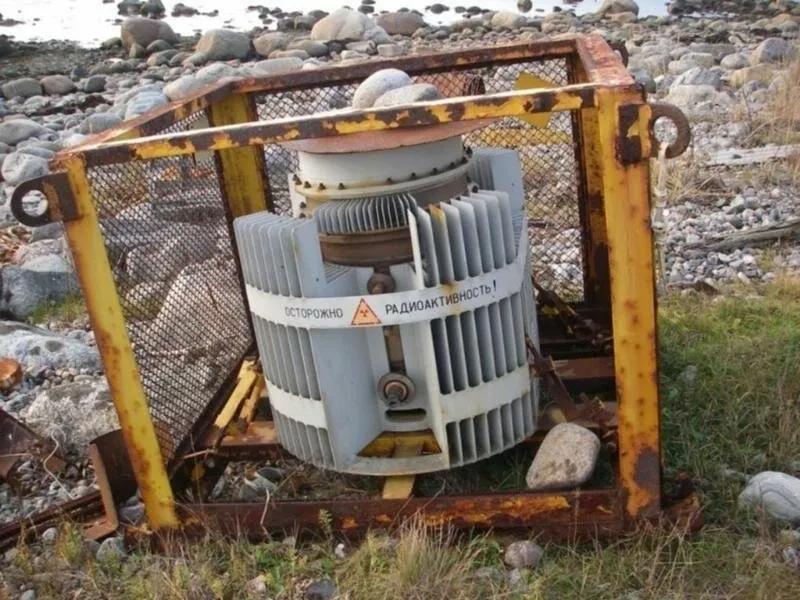

Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generators (RTGs) have been used in a variety of applications, including in the military, where reliability and longevity are crucial factors. The M-type RTG, in particular, was used to power navigation systems in military vehicles and equipment using the radioactive isotope Strontium-90.
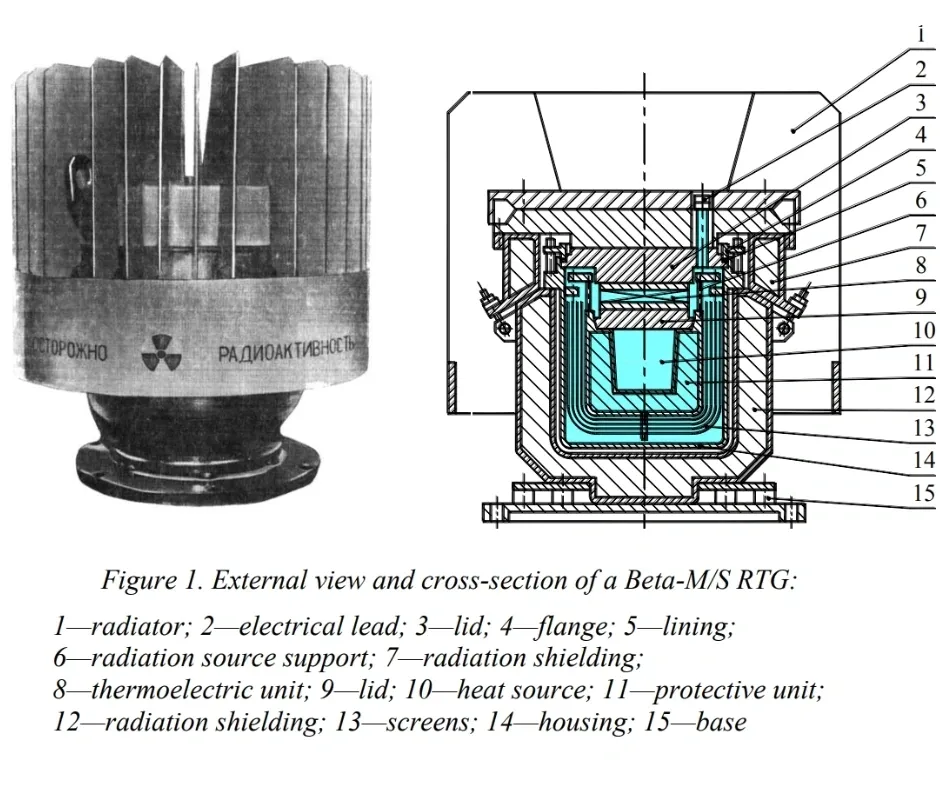 Figure 1. Components of RTG
Figure 1. Components of RTG
In the late 1950s, the United States military developed a portable RTG that used Strontium-90 as a radioactive heat source. The resulting electricity was converted using a thermocouple and used to power military equipment, including communication and navigation systems.
The M-5 RTG was developed in the 1960s to power the AN/URC-64(V) communication system used by the US Navy. The RTG used Strontium-90 as its radioactive heat source, providing long-lasting power to the communication system in remote locations.
The Soviet Union also developed their own Strontium-90-powered RTGs for use in military applications. The Soviet RTGs were similar in design to those developed by the United States, with Strontium-90 as the radioactive heat source and a thermocouple to convert the heat into electricity. The Soviet Union used Strontium-90 powered RTGs in their military communication and navigation systems, providing reliable power in remote locations.
The use of Strontium-90-powered RTGs in military navigation systems allowed for precise navigation even in GPS-denied environments. The AN/ASN-58A Inertial Navigation System used Strontium-90 powered RTGs to provide electricity to the system’s gyroscopes and accelerometers, while the Transit satellite navigation system used Strontium-90 powered RTGs to provide electricity to the system’s satellites.
Despite concerns about the risk of radioactive contamination, the use of Strontium-90-powered RTGs in military navigation systems continued for several decades. Advances in technology have led to the development of safer and more efficient RTGs, making them a promising option for powering critical systems and equipment in remote locations.
In conclusion, the use of Strontium-90-powered RTGs in military navigation systems provided reliable and long-lasting power in remote locations, allowing for precise navigation even in GPS-denied environments. The development of the M-type RTG using Strontium-90 has been a significant milestone in the history of RTGs and its contribution to military navigation systems has been invaluable.
RadSentric Sdn Bhd is a licensed Training & Consultation company registered under Jabatan Tenaga Atom (ATOM Malaysia) with License H (LPTA/A/3763).
